From 4G Mobile Technology to 5G: The Evolution of Wireless Communication
Mobile communication has become an essential part of modern life. From making phone calls and sending messages to streaming videos, online gaming, and remote work, mobile networks support almost every digital activity today. Over the years, mobile technology has evolved rapidly, with each generation bringing major improvements. The shift from 4G (Fourth Generation) to 5G (Fifth Generation) represents one of the most significant changes in the history of wireless communication. This transition is not just about faster internet speeds; it is about transforming how people, devices, and industries connect with each other.
Understanding 4G Mobile Technology
4G technology, also known as LTE (Long Term Evolution), was introduced to provide faster data speeds, better connectivity, and improved user experience compared to 3G. It enabled high-quality video streaming, online gaming, video calls, and smooth browsing on smartphones.
With 4G networks, users experienced download speeds ranging from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps, depending on network conditions. This speed made it possible to use applications like YouTube, Netflix, Zoom, and social media platforms efficiently. 4G also reduced latency (delay), allowing real-time communication and better performance for mobile apps.
Another important feature of 4G was its ability to support multiple devices simultaneously. As smartphones became more powerful and affordable, the number of internet users increased rapidly. 4G networks successfully handled this growth for many years, becoming the backbone of modern mobile communication.
However, as technology continued to advance, the limitations of 4G became more visible.
Limitations of 4G Networks
Although 4G brought major improvements, it was not designed to handle the massive number of connected devices and data-heavy applications we see today. Some key limitations of 4G include:
- Limited Speed: While fast, 4G cannot meet the demands of emerging technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and ultra-high-definition streaming.
- Higher Latency: 4G latency is usually around 30–50 milliseconds, which is not ideal for applications requiring instant response, such as autonomous vehicles or remote surgeries.
- Network Congestion: With billions of smartphones and IoT devices, 4G networks can become congested, leading to slower speeds in crowded areas.
- Limited Support for Smart Technologies: 4G was not designed to fully support smart cities, massive IoT networks, and advanced automation.
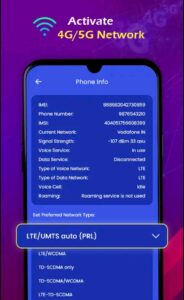
To overcome these challenges, a new generation of mobile technology was required—this led to the development of 5G.
What Is 5G Technology?
5G stands for Fifth Generation mobile network. It is designed to deliver extremely fast speeds, ultra-low latency, and the ability to connect a massive number of devices at the same time. Unlike previous generations, 5G is not only focused on smartphones but also on machines, vehicles, sensors, and entire industries.
5G networks can provide download speeds of up to 10 Gbps, which is nearly 100 times faster than 4G in ideal conditions. Latency in 5G can be as low as 1 millisecond, making real-time communication almost instantaneous.
5G uses advanced technologies such as millimeter waves, small cells, massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), and beamforming to deliver high performance and efficiency.
Key Differences Between 4G and 5G
The transition from 4G to 5G brings several important improvements:
1. Speed
4G offers good speed for everyday tasks, but 5G provides ultra-fast data rates that enable instant downloads, smooth 4K/8K streaming, and advanced gaming experiences.
2. Latency
5G drastically reduces latency compared to 4G. This improvement is crucial for applications that require real-time responses, such as self-driving cars and remote medical procedures.
3. Capacity
5G can support millions of devices per square kilometer, making it ideal for smart cities, IoT devices, and large public events.
4. Reliability
5G networks are more stable and reliable, ensuring consistent performance even in high-demand situations.
5. Energy Efficiency
5G technology is designed to consume less power, which helps extend battery life for devices and reduces environmental impact.
Impact of 5G on Daily Life
The introduction of 5G will significantly change how people use technology in their daily lives. Faster speeds and low latency will improve video calling, online education, and remote work. Cloud-based applications will run more smoothly, and users will be able to access high-quality content instantly.
Download
Mobile gaming will reach a new level with real-time multiplayer games and cloud gaming services that require no downloads. Augmented reality and virtual reality applications will become more common in education, entertainment, and training.
Role of 5G in Industry and Economy
One of the biggest advantages of 5G is its impact on industries. It is expected to play a key role in Industry 4.0, enabling smart factories, automation, and robotics. Machines will be able to communicate with each other in real time, improving productivity and reducing costs.
In healthcare, 5G can support remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and even robotic surgeries. Doctors will be able to provide care to patients in distant locations with high precision.
In transportation, 5G will enable connected and autonomous vehicles, improving road safety and traffic management. Vehicles will communicate with each other and with traffic systems to reduce accidents and congestion.
Agriculture will also benefit from 5G through smart farming techniques, such as real-time soil monitoring, automated irrigation, and drone-based crop analysis.
Challenges in the Transition from 4G to 5G
Despite its benefits, the transition from 4G to 5G faces several challenges. Building 5G infrastructure requires significant investment, including new base stations, fiber networks, and equipment. Since 5G uses higher frequency bands, it has a shorter range, which means more towers are needed.
Another challenge is device compatibility. Not all smartphones support 5G, so users need to upgrade their devices to enjoy 5G services. Additionally, in many developing countries, 4G is still expanding, and full 5G deployment may take time.
Security and privacy are also important concerns. As more devices connect to the network, protecting data and preventing cyberattacks becomes more critical.
The Future Beyond 5G
While 5G is still being deployed globally, researchers are already working on future technologies like 6G. These future networks aim to provide even higher speeds, smarter connectivity, and deeper integration with artificial intelligence.
However, for now, 5G represents a major milestone in mobile communication. It builds upon the foundation of 4G and opens the door to innovations that were previously impossible.
Conclusion
The transition from 4G mobile technology to 5G marks a revolutionary step in the evolution of wireless communication. While 4G transformed smartphones and mobile internet, 5G goes far beyond, enabling smart cities, advanced healthcare, automation, and immersive digital experiences. With faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity, 5G is set to reshape how we live, work, and interact with technology.
Although challenges remain in infrastructure, cost, and security, the benefits of 5G far outweigh the difficulties. As 5G continues to expand across the world, it will play a crucial role in driving digital growth and innovation for years to come.